

C.Nyburg: Private communication and Brit. 15 G.Herzberg: Spectra of Diatomic Molecules (D.In this session, Vivek Sir will be covering Crystal Lattice and Unit Cell from the Solutions chapter. Hence the number of atoms per unit cell 8 × (1/8) 1 only. Therefore, the contribution of each atom to the unit cell 1/8. Each atom is equally shared by eight atoms because each cube contains eight corners.
CRYSTAL LATTICE SERIES
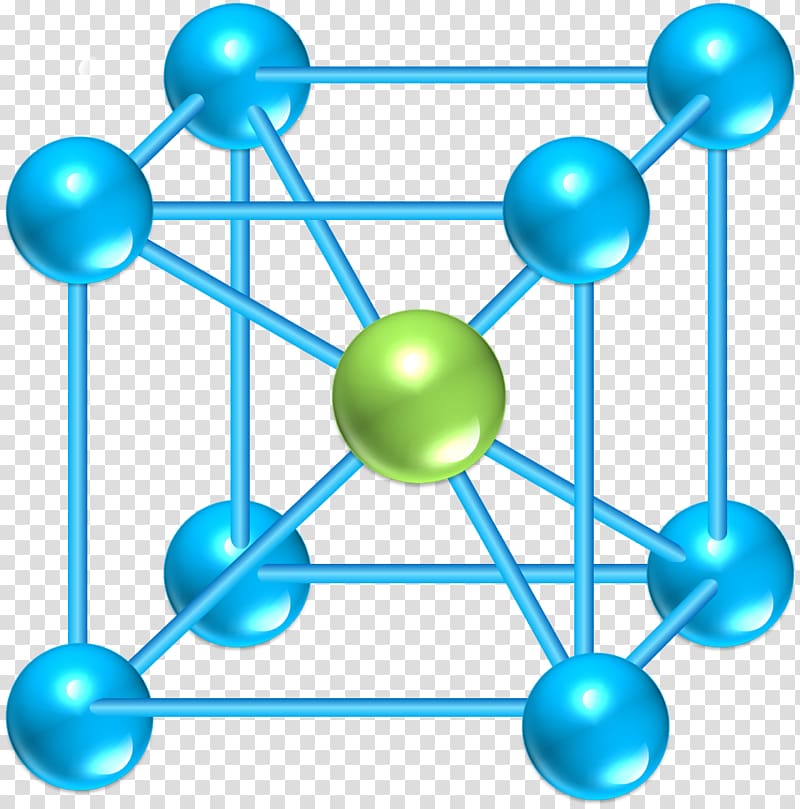
11 L.Pauling: The Nature of the Chemical Bond, 3rd ed.B.Bird: Molecular Theory of Gases and Liquids (John Wiley and Sons, Inc., New York, 1954) Google Scholar I.Kitaigorodskii, V.Khotsynova and M.Struchkov: Zhur. A rough estimate of the energy due to partial covalent bonding was made and is shown to be quite important for the stability. Formation of partial covalent bonds between molecules in this structure, but not in the cubic structure, may account for the stability of the former. Possible inappropriate ratio between the two coefficients in the Lennard-Jones potential does not seem to account for the observed stability of the orthorhombic structure. A similar situation was found for iodine. Thus, the cubic structure has a little lower energy than the orthorhombic structure. A Lennard-Jones type potential was assumed between nuclei of the interacting molecules. The lattice energy of the crystals of halogen molecules Cl 2 and I 2 is calculated for orthorhombic structure (space group Bmab ) and cubic structure (space group P a 3) by varying lattice parameters ( a, b, c, and the orientation angle, ϕ, of the molecular axes) and finding the minimum of the energy. Solid State (Lec-4) || Analysis of Cubic System &.Solutions (Lecture-1) | Classification, Solubility.Solid State (Lecture-5) | Relation b/w Edge Length.Solid State (Lecture-3) | Crystal Lattice, Unit Ce.Solution (Lec-3) | Numerical Approach regarding He.Solution (Lecture-4) | Vapour Pressure & Factors a.Solution (Lec-5) | Raoult's Law and Calculation of.An atom in a simple cubic lattice structure contacts six other atoms, so it has a coordination number of six. For a polonium atom in a simple cubic array, the coordination number is, therefore, six. Solution (Lec-6) | Numerical approach Using Raoult. The number of other particles that each particle in a crystalline solid contacts is known as its coordination number.Solution (Lecture-7) | Ideal & Non-ideal Solutions.Solution (Lecture-8): Colligative Properties of El. The number of other particles that each particle in a crystalline solid contacts is known as its coordination number.Solution (Lecture-9) | PYQs related to Colligative.Solution (Lec-10) || Relative Lowering in Vapour P.This smallest repeating unit (unit cell) represents. Unit Cell is the smallest repeating unit in space lattice or crystal lattice which when repeated over and over, again produces the complete crystal lattice. Mole Concept || Formula Mass | Avogadro Number | M. Crystal lattice is a regular arrangement of the constituent particles (atom, ions, or molecules) in a solid in three-dimensional space.Mole Concept | Molar Mass | Lecture-6 | NEET, JEE.Mole Concept |(Lecture 7) Procedure For Solving Pr.Concentration Terms || Molarity | Molality | Equiv.Molarity, Molality, Normality & it's Numericals |.
Formality, Mole Fraction | Lecture-10 || Class 11.#Rhythm_Education #Yogesh_Maurya #Solid_State #space_lattice #Unit_cell #Bravais_lattices #Cubic_system #Chemistry #NEET #IIT_JEE #Class12 #CBSE #ICSE #IIT_JAM #NET #GATE #TIFR #BARK #PGT Thank you for joining and staying with us. Crystal lattice definition: the regular array of points about which the atoms, ions, or molecules composing a. Please Like, Comment, Share and Subscribe. If you have any doubt, let me ask freely in the COMMENT box. I hope this information will help you in your preparation. Crystal Structure 1 3.1 Some Basic Concepts of Crystal Structure: Basis and Lattice A crystal lattice can always be constructed by the repetition of a fundamental set of translational vectors in real space a, b, and c, i.e. In this particular video, we discuss about Formation of crystal and crystal system, Space lattice or Crystal lattice, Unit cells and it's types, Bravais lattices corresponding to different crystal system in details. Namaskaram Everyone, this is Yogesh Maurya and Welcome to the Rhythm Education.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
